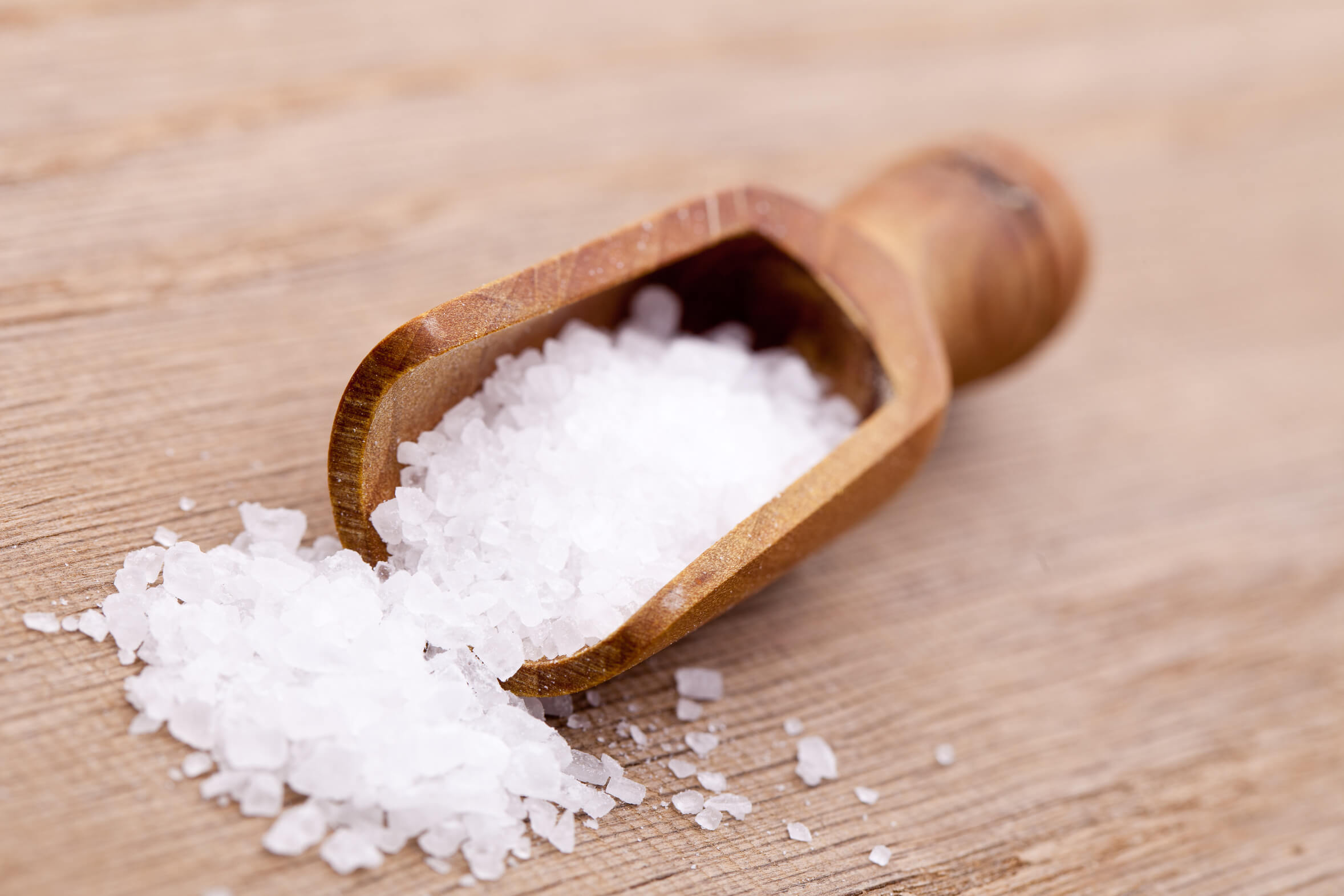
synonyms: botanical family: origin: Classification: spice shape: taste: odour: use: When seasoning with salt you have to be especially careful, the dish will quickly become salty. In particular, it should be known that salt increases the cooking temperature of water and thus removes the liquid from meat and some vegetables. Another characteristic of salt is its preservative property. It dissolves completely in liquid and gains in concentration as soon as this liquid has evaporated. This is also how the principle of sea salt production works. This also explains why if you season a dish with salt too early, you can quickly spoil it. Nevertheless, salt is one of the oldest remedies of mankind. Its health-promoting properties are extremely varied. Salt not only regulates our fluid balance, but also the hormone balance and the internal organs. The human body consists of 75 percent salty liquid, so salt is indispensable for maintaining our vital functions. tip: Recipe suggestion: knowledge: Home & Distribution: cultivation & extraction: History: Sea salt
 Botanical name:
Botanical name:
Sodium chloride
cooking salt, table salt
sea salt
Oceans or mines
salt
Mineral
salty
odourless
Salt is used in almost every dish. Even with sweet dishes it rounds off the taste. Salt is also used for preservation.
Put a few grains of rice in the salt mill, so that it does not clump
Fish in salt crust: Wash the gilthead or salmon trout and fill with finely chopped fresh herbs (dill, parsley, lemon balm) and 1 lemon in slices. Lightly beat 3 egg whites with 2-3 kg coarse sea salt. Lay out the ALU-foil on a baking tray. Spread 1/3 of the salt mixture on it and place the fish on top. Cover the fish on all sides with the rest of the salt. Bake at 200° for about 40 minutes. Tap the salt crust on the back with a knife and carefully lift it off. Remove the skin and serve.
Extraction: 20% of the salt production comes from sea water through evaporation of so-called sea salt, rock salt is extracted in mines and accounts for about 70% of the world production. Original salt is a natural, unpurified salt (e.g. so-called Himalayan salt).
The history of salt begins in the Neolithic Age. Man went in search of salt.
Salt is found in salty soils, in the sea and in salt domes. After the Neolithic Age, salt was already mined from salt pieces and skimmed from the sea, as it is still done today.
The first indirect encounter with salt was when people lived on the meat of wild animals. The mineral salts that the human organism needs to survive were contained in the meat of the killed animals. It was only when people discovered their interest in cereals as food that they needed salt, as field crops do not contain enough mineral salts.
http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Speisesalz