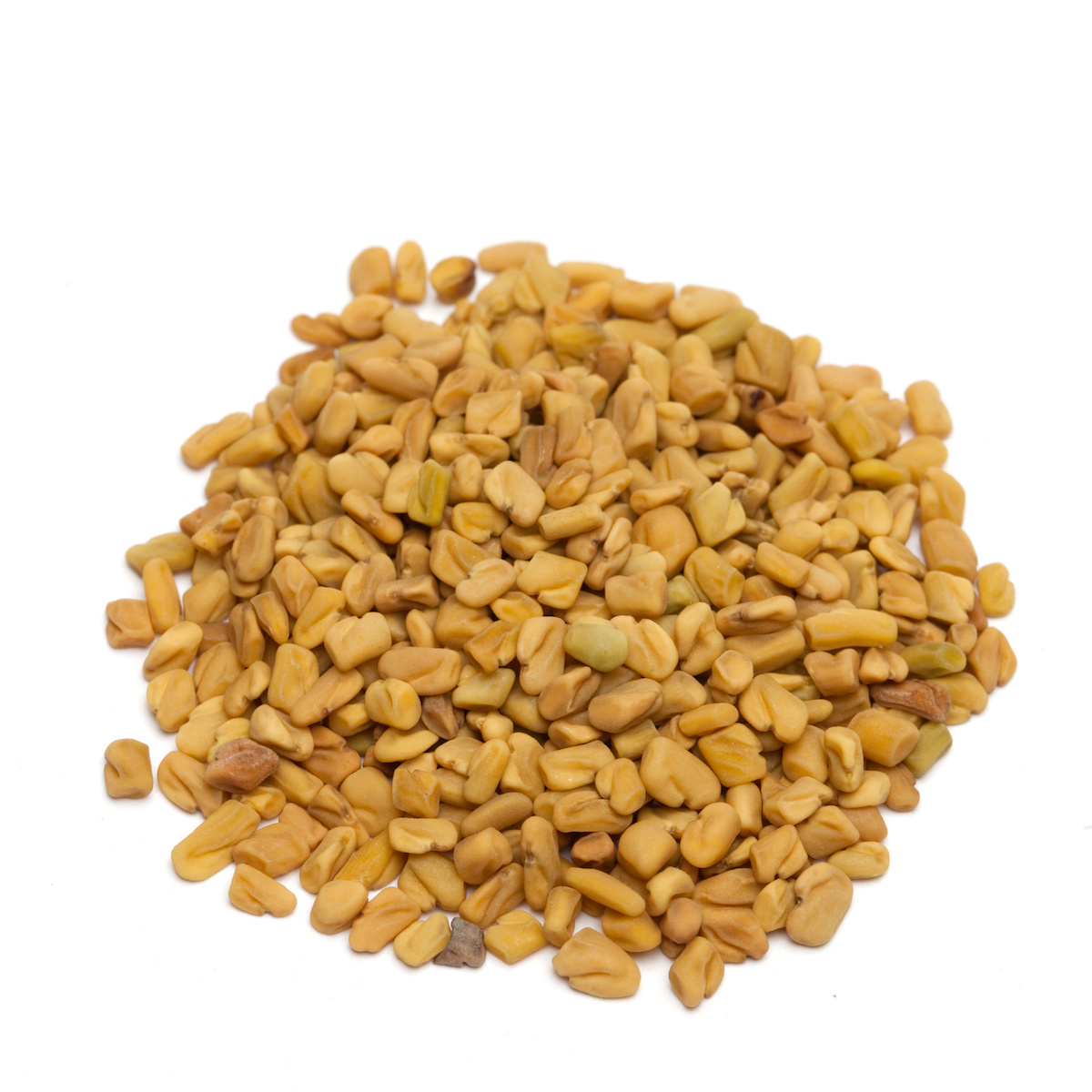
Botanical name: Synonyms: Botanical family: origin: Classification: spice shape: flavor: odor: use: In dry countries in the Middle East, North Africa and Spain, fenugreek is cultivated as a food or fodder plant and is roasted, boiled or eaten fresh. It also tolerates a high degree of soil salinity. In addition, it is used as a spice and is an essential ingredient of curry powder, for example. Likewise, the seeds - like blue fenugreek - are used as a spice for bread or cheese in South Tyrol, for example. Fenugreek is a component of a spice mixture for the production of the Turkish dried meat specialty Pastırma. The sprouts are added to salads as a seasoning ingredient. tip: Recipe suggestion: knowledge: Botany: home & distribution: cultivation & extraction: History: Fenugreek
General information
Application
Things to know

Trigonella foenum-graecum L.
Greek hay, cow horn clover
butterfly blossom plants
Mediterranean countries
spice
seed
slightly hot, bitter
spicy
ingredient of curry dishes and chutneys
Fresh fenugreek leaves can be kept in plastic bags in the refrigerator for a few days
Indian potato soup: 500 g potatoes and 2 carrots cut into small pieces. Fry in 30 g butter. Season with salt, 1 tsp. curry and 1 tsp. fenugreek. Deglaze with 3/4 l broth and cook on low heat for 15 minutes. Puree part of the soup and sprinkle 1/2 bunch of spring onions over it.
Sports: Known by bodybuilders as "Fenugreek". An appetite stimulating and testosterone increasing effect is discussed.
Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) belongs to the subfamily of papilionaceous plants (Faboideae) within the family of legumes (Fabaceae). Fenugreek is closely related to the blue fenugreek (Trigonella caerulea)
Fenugreek is spread over southern Europe, Africa, the Middle East, India, China and Australia. Main cultivation areas are Morocco and India. Still today, the fenugreek occurs wildly as far as in southern and middle Germany. Smaller quantities are also cultivated for still teas and other purposes in Germany (100ha) and France (500ha).
Fenugreek grows as an annual herbaceous plant that reaches a height of 30 to 80 centimeters. The whole plant has a strong smell. It develops a long tap root and fibrous lateral roots. The upright, round stems are branched.
Fenugreek was already domesticated in the Chalcolithic, charred seeds originate from Tell Halaf. Iron Age evidence was found in the Tell of Deir Alla in the Jordan Valley. It was also used in ancient Egypt, where it played a role in herbal medicine and obstetrics as well as in religious acts. Arab doctors taught that after applying boiled fenugreek seeds, dandruff and hair loss were reduced and the hair became curly.
http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bockshornklee